- Mon - Sat: 9:00
- Call Us: +90 (538) 894 00 91
- [email protected]
Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopy is a surgical procedure in which the inside of the joint is visualized and diseases are diagnosed and treated. It comes from two Greek words; “arthro” (joint) and “skopein” (to look into).
Picture Arthroscopy tower
In arthroscopic examination of the joint, the orthopedist views the inside of the joint through small wounds with pen-like instruments. Structures such as cartilage and ligaments within the joint can be visualized larger on the screen. Thus, pathological structures can be recognized more easily and accurately. In addition, necessary treatments can be performed through small incisions.
Arthroscopy is now routinely performed in many large joints such as the knee, shoulder, ankle, elbow and hip joints.
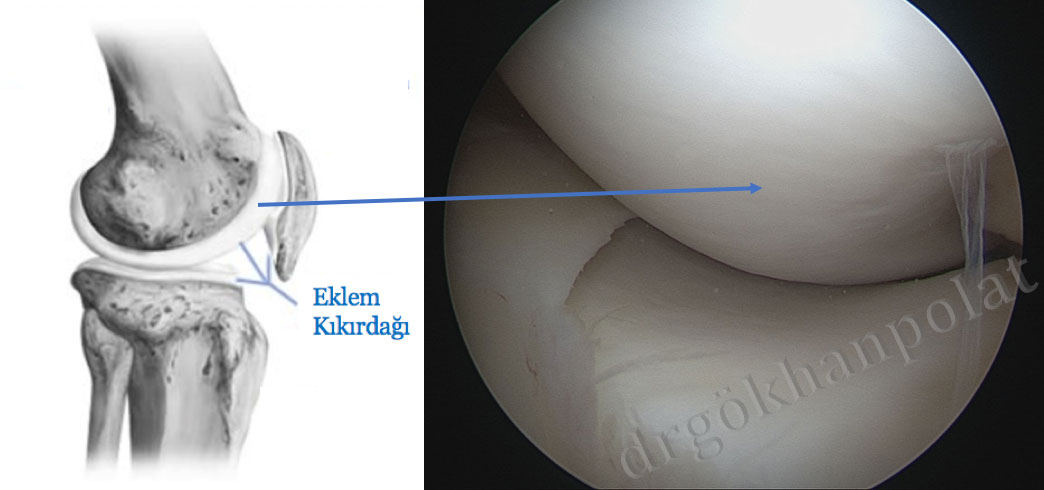
Nowadays, many joint diseases can be diagnosed using MRI. In this regard, arthroscopy is often used in treatments where surgical procedures can be performed through smaller incisions. This allows patients to experience a more comfortable and faster recovery period. Nevertheless, arthroscopy is still used for diagnostic purposes in some cartilage pathologies.
Today, there are many surgical treatments performed with the help of arthroscopy. Commonly performed treatments include: