What Is Total Hip Replacement?
A Permanent Solution for Chronic Hip Pain
Total hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which a severely damaged or worn hip joint is replaced with an artificial implant (prosthesis). It is performed in patients whose hip pain and mobility issues significantly impair their daily activities and quality of life—often due to advanced arthritis or joint degeneration.
With modern techniques and materials, total hip replacement surgery provides long-term pain relief, improves mobility, and helps patients regain independence and functionality.
Anatomy of the Hip Joint and Degeneration
The hip is one of the body’s largest and deepest joints. It forms where the femoral head (top of the thigh bone) meets the acetabulum (hip socket). A smooth cartilage surface covers these bones, allowing frictionless and pain-free movement.
Over time, due to various conditions such as:
- Osteoarthritis
- Hip fractures
- Developmental dysplasia (hip dislocation)
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Avascular necrosis (bone death)
the cartilage wears away, the joint space narrows, and pain increases with movement. When conservative treatments like medications and physical therapy fail, hip replacement surgery becomes the next step.
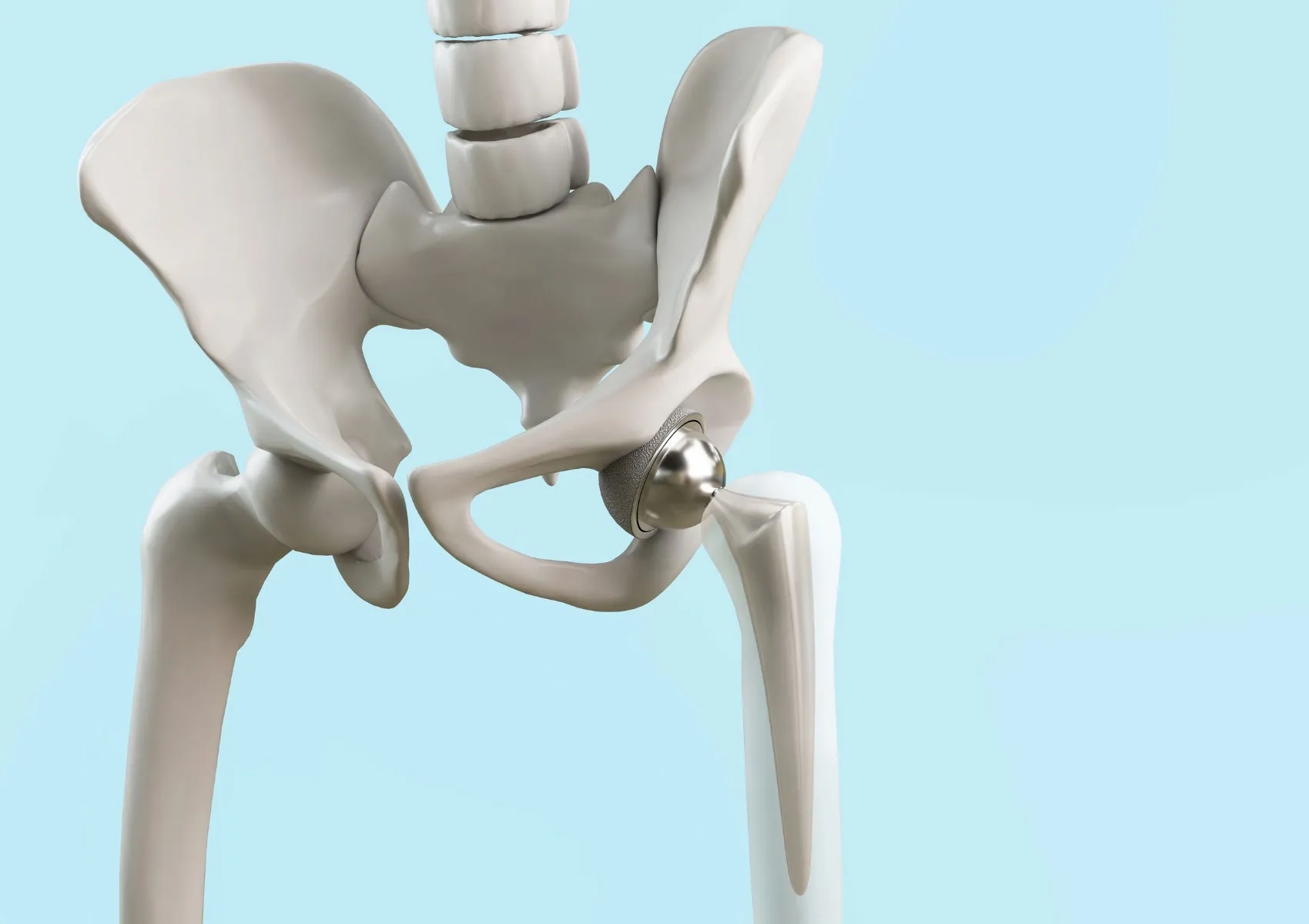
What Is Total Hip Replacement?
In a total hip replacement, both the femoral head and the acetabulum are replaced with artificial components. The prosthesis generally consists of two main parts:
- Femoral Component: A metal or ceramic ball mounted on a stem inserted into the femur
- Acetabular Component: A socket placed in the pelvis, made of metal, plastic, or ceramic
These components mimic natural joint movement, reduce pain, and restore function.
When Is Total Hip Replacement Recommended?
- Severe pain during daily activities (walking, dressing, sitting)
- Pain that persists even at rest
- X-rays showing joint space narrowing and bone deformity
- No improvement with non-surgical treatments
- Significant reduction in range of motion
- Chronic limping or stiffness around the hip
Benefits of Total Hip Replacement
- Significant reduction in hip pain
- Restoration of joint movement and flexibility
- Enhanced quality of life
- Ability to perform daily tasks independently
- Return to walking, climbing stairs, and participating in social activities
Who Is a Candidate for Hip Replacement?
- Typically patients aged 55 and older
- Individuals with severely damaged joints who haven’t responded to other treatments
- Patients with hip fractures and disrupted joint surfaces
- People with significantly limited range of motion in the hip
- Those in good overall health and fit for surgery
What to Expect After Surgery
- Hospital stay: Usually 2–4 days
- Walking: Supported walking may begin on the first day
- Physical therapy: Starts early in recovery
- Return to normal activities: 4–6 weeks
- Sport and high-impact activities: After 3 months with physician guidance
- Prosthesis lifespan: Typically 15–20 years, depending on material and patient activity
Types of Prosthetic Materials
- Metal-on-metal
- Metal-on-polyethylene (plastic)
- Ceramic-on-ceramic
- Ceramic-on-polyethylene
The choice of material depends on age, activity level, bone quality, and surgeon preference.
FAQ
-
How long does the hip replacement surgery take?
The procedure typically lasts between 1 and 2 hours.
-
Can I play sports after hip replacement?
Yes. Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are encouraged. High-impact or contact sports should be avoided.
-
How long does a hip prosthesis last?
On average, 15–20 years. Newer materials may last even longer.
-
Is there pain after surgery?
Some discomfort is expected in the early days but is usually well-controlled with medications.
-
Will there be leg length differences after surgery?
Minor discrepancies may occur but are usually corrected during surgery to ensure proper alignment.