Total Knee Replacement: Preoperative and Postoperative Considerations
Planning for total knee replacement? Discover essential preoperative tips, surgical details, and expert guidance for smooth recovery after knee replacement surgery.
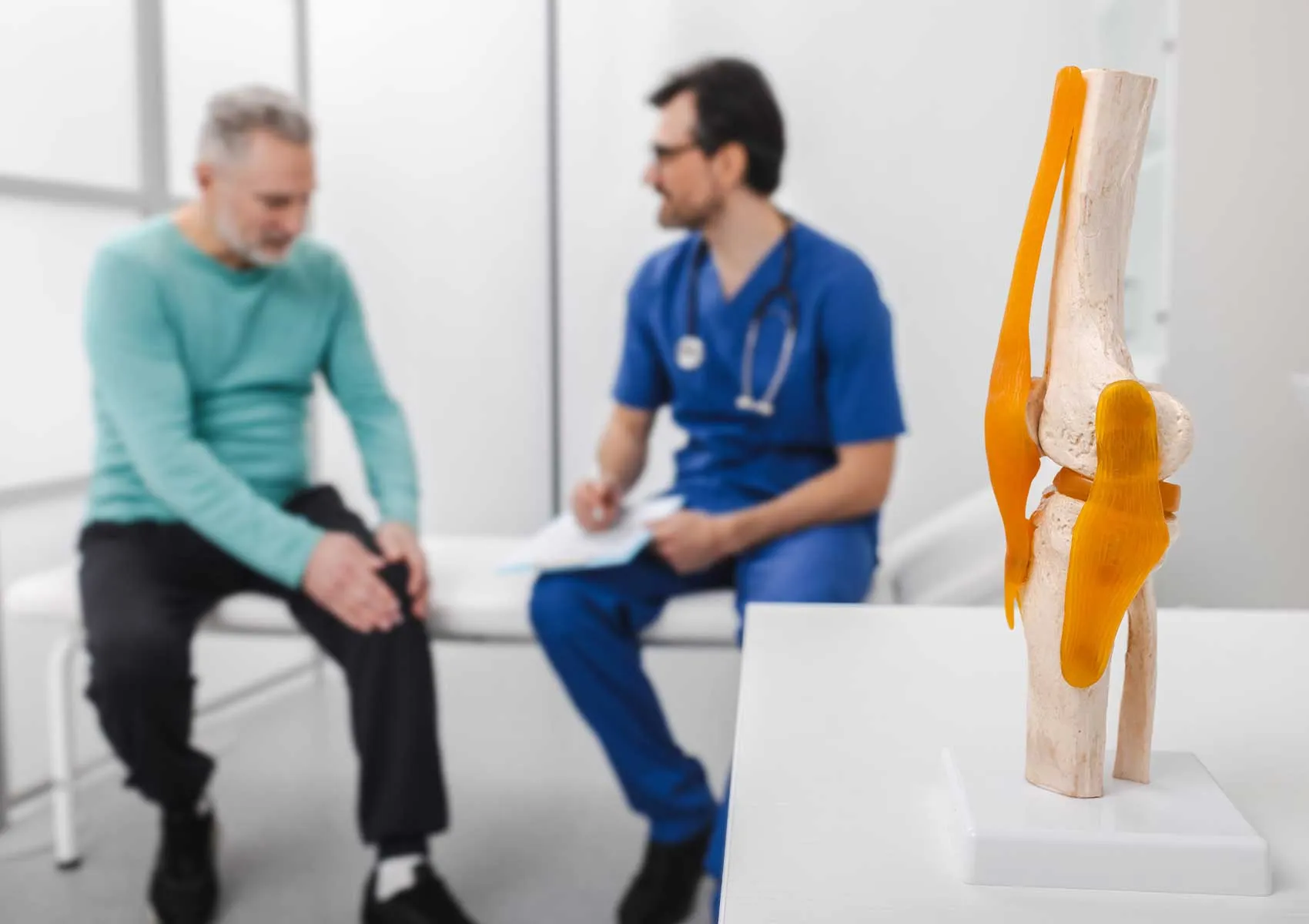
Total knee replacement (TKR) is a highly effective surgical procedure for patients suffering from severe knee arthritis, cartilage damage, or deformity that significantly impairs daily function. When conservative treatments such as medication, injections, and physical therapy fail to provide relief, TKR becomes the treatment of choice. However, the success of the procedure depends not only on the surgery itself but also on comprehensive preoperative preparation and diligent postoperative rehabilitation.
This article offers a detailed overview of the total knee replacement process before and after surgery, highlighting important steps for a smooth recovery.
What Is Total Knee Replacement?
In a total knee replacement, the damaged surfaces of the femur, tibia, and often the patella are replaced with metal and plastic components that mimic the natural movement of the knee. This surgical procedure:
- Relieves chronic pain
- Restores mobility
- Corrects deformities (e.g., bowed legs, leg length differences)
- Improves overall quality of life
It is typically performed in cases of advanced osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or post-traumatic joint degeneration.
Preoperative Phase
1. Medical Evaluation
A comprehensive medical assessment ensures surgical safety and includes:
- Blood tests, urine analysis
- Chest X-ray and EKG
- Cardiologic or endocrinologic clearance for comorbidities like diabetes or hypertension
- Anesthesia consultation and risk stratification
2. Physical Preparation
- Weight loss if the patient is overweight
- Prehabilitation: strengthening of quadriceps and hamstring muscles
- Treating any active infections (e.g., urinary, dental)
- Smoking cessation at least several weeks before surgery
3. Patient Education
- Understanding the surgical process and realistic expectations
- Preparing the home for safe mobility (elevated toilet seat, grab bars)
- Learning how to use assistive devices such as walkers or canes
- Mental preparation for recovery and participation in physiotherapy
The Surgery Itself
The procedure typically takes 1 to 2 hours under general or spinal anesthesia.
Surgical Technique
- A midline incision is made on the front of the knee
- The joint is exposed and the damaged cartilage is removed
- Prosthetic components are fixed to the bones (cemented or cementless)
- Drain placement and closure follow
Postoperatively, patients are mobilized early, usually within 24 to 48 hours.
Postoperative Recovery
1. Hospital Phase (First Days)
- Pain management and blood clot prevention begin immediately
- Physical therapy is initiated to begin range-of-motion and walking exercises
- Drains are removed, and dressings are changed regularly
- Patients typically stay in the hospital for 3–5 days
2. First 6 Weeks
- Walking with assistive devices
- Gradual increase in daily activities
- Basic functional tasks like sitting, standing, and stair climbing
- Stitches or staples removed around 10–14 days
3. 6 Weeks to 3 Months
- Assistive devices may no longer be necessary
- More advanced muscle strengthening and balance training
- Improved knee flexion and extension
- Noticeable reduction in pain and stiffness
4. After 3 Months
- Near-normal mobility
- Resumption of light sports (e.g., walking, swimming, cycling)
- Full recovery is typically achieved within 6–12 months
Importance of Rehabilitation
Successful surgery must be complemented by a structured rehabilitation program. Failure to adhere to a proper protocol may result in:
- Limited range of motion
- Persistent pain or stiffness
- Weakness and balance problems
- Delayed return to normal function
A physiotherapist-guided rehab plan that includes range-of-motion exercises, ice therapy, gradual loading, and strength-building is critical.
FAQ
-
When can I start walking after total knee replacement?
Patients usually begin walking with assistance within 1–2 days post-surgery.
-
How long will I stay in the hospital?
The typical hospital stay ranges from 3 to 5 days, depending on recovery speed and individual health.
-
Can I drive after knee replacement surgery?
Most patients resume driving within 6–8 weeks, depending on strength and reaction time.
-
Is the surgery risky?
Like all surgeries, TKR has risks, but complication rates are low in experienced hands and with proper preparation.
-
How long does a knee prosthesis last?
Modern implants typically last 15–20 years, depending on activity level and joint care.