Robotic Surgery in Hip Replacement
This article explores robotic-assisted hip replacement surgery, detailing its process, benefits, and clinical outcomes supported by current orthopedic research.
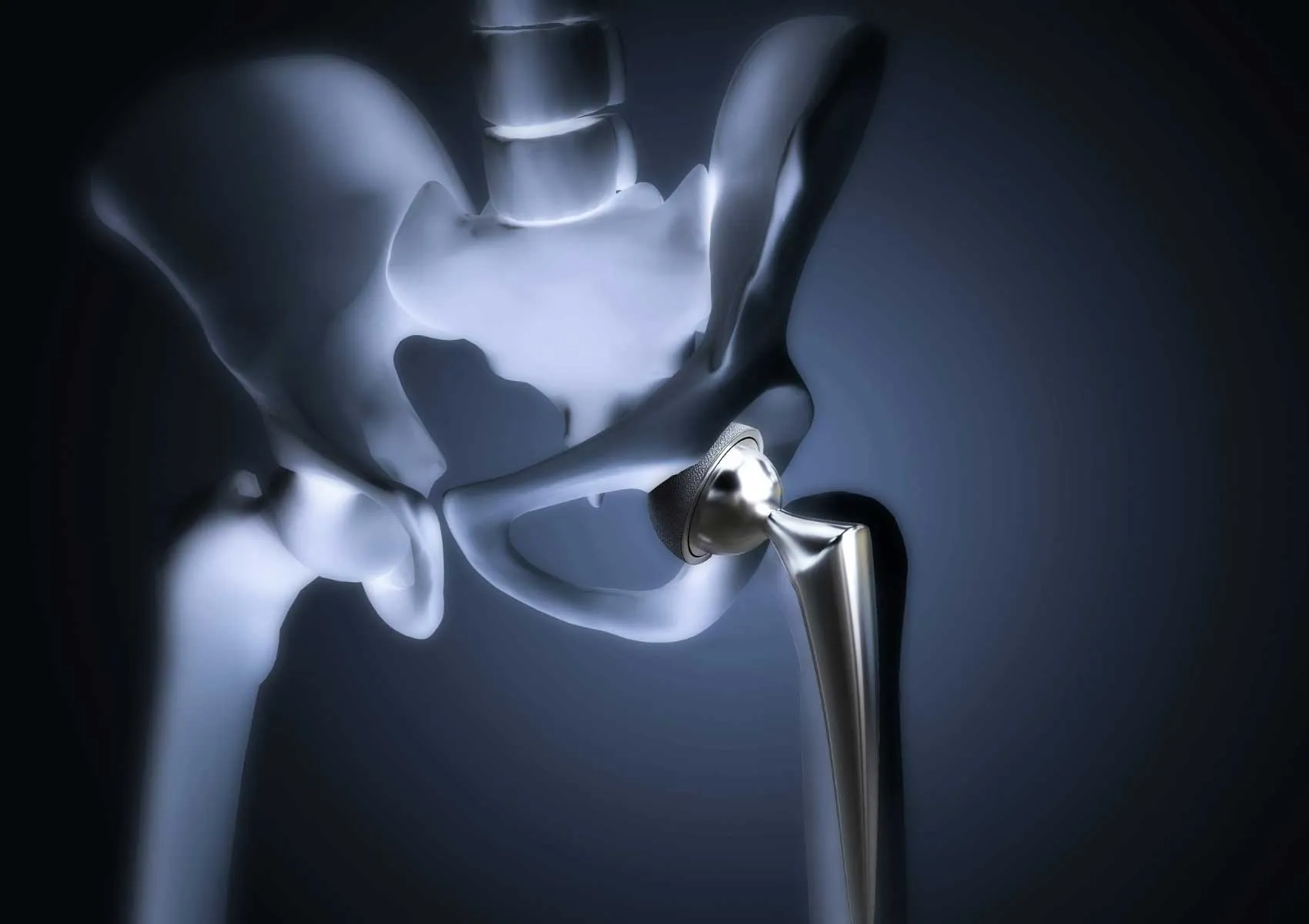
Hip replacement surgery is a well-established treatment for conditions such as advanced osteoarthritis, avascular necrosis, post-traumatic deformities, or inflammatory joint diseases. While conventional surgical techniques have delivered successful results for decades, the integration of robotic technology into hip replacement procedures has significantly enhanced surgical precision, individualization, and functional outcomes.
Robotic-assisted hip replacement combines a surgeon’s experience with the accuracy of cutting-edge technology to optimize surgical results. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of robotic surgery in hip arthroplasty, its benefits, ideal patient profiles, and the procedural steps involved.
What Is Robotic-Assisted Hip Surgery?
Robotic surgery utilizes computer-guided systems that enhance precision and consistency in orthopedic operations. In hip replacement, semi-active robotic systems are commonly used. These systems:
- Allow the surgeon full control of the operation with robotic guidance
- Generate a 3D model of the patient’s hip anatomy using preoperative CT scans
- Calculate the optimal implant placement and angles with millimeter-level accuracy
The robot ensures that bone cuts and implant positions follow the surgical plan precisely, helping reduce human error during the procedure.
Key Phases of Robotic Hip Replacement
Robotic-assisted hip replacement includes several distinct stages:
1. Preoperative Imaging and Planning
Before the surgery, the patient undergoes a CT scan to construct a detailed 3D model of their hip anatomy. This enables:
- Identification of deformities and irregularities
- Patient-specific surgical planning
- Targeted restoration of leg length and joint alignment
2. Intraoperative Robotic Guidance
During surgery, the robotic system assists without restricting the surgeon’s control. It:
- Guides the surgeon to make accurate bone cuts
- Ensures precise positioning of the implant
- Detects deviations from the pre-set plan in real time
This guidance allows for anatomically optimized prosthesis placement.
3. Real-Time Feedback
The system provides intraoperative data on:
- Joint stability
- Leg length measurements
- Soft tissue balance
These features contribute to minimizing postoperative complications and improving patient outcomes.
Advantages of Robotic Hip Replacement
Compared to traditional techniques, robotic-assisted hip surgery offers several compelling advantages:
- Enhanced accuracy: Implants are placed with high precision, improving alignment and function.
- Leg length symmetry: Reduced risk of leg length discrepancy after surgery.
- Minimal soft tissue damage: Robotic tools enable targeted exposure, preserving surrounding structures.
- Longer implant lifespan: Optimal positioning reduces implant wear and loosening.
- Faster recovery: Less tissue disruption often results in quicker rehabilitation.
- Lower revision rates: Proper alignment reduces the likelihood of future corrective surgery.
These benefits are especially significant for younger, active patients seeking durable and reliable outcomes.
Who Can Benefit from Robotic-Assisted Hip Surgery?
While robotic surgery offers many advantages, it may not be suitable for everyone. Ideal candidates include:
- Patients with end-stage hip arthritis
- Individuals with significant leg length discrepancy
- Patients with complex hip anatomy
- Those undergoing revision surgery
- Active individuals desiring optimal joint function and precision
In cases of abnormal or previously operated anatomy, robotic systems provide superior surgical control.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite its advantages, robotic surgery has certain limitations:
- Cost: Robotic procedures can be more expensive due to technology use.
- Required experience: Surgeons must be trained in robotic systems for optimal results.
- Limited availability: These systems are currently available in select centers.
Patients should consult experienced orthopedic teams and confirm whether robotic technology is available at their chosen facility.
What Does the Science Say?
Clinical studies support the use of robotic systems in hip replacement surgery. Research indicates:
- Implant positioning accuracy exceeds 95%
- Lower incidence of leg length discrepancy (LLD)
- Reduced complication and revision rates
- Higher early-stage patient satisfaction and function
These outcomes depend greatly on the experience of the surgical team and adherence to best practices.
FAQ
-
What is the difference between robotic and traditional hip surgery?
Robotic surgery uses 3D planning and computer guidance for more accurate implant positioning.
-
Is robotic hip replacement safer?
Yes, it offers better precision, leading to lower complication rates.
-
Does robotic surgery result in faster recovery?
Often yes, due to less soft tissue disruption and better implant alignment.
-
Can all patients undergo robotic hip surgery?
No, patient selection depends on anatomy, overall health, and facility availability.
-
Are robotic systems reliable?
Clinical data supports their accuracy, consistency, and long-term benefits in experienced hands.